734 1-800-452-1261
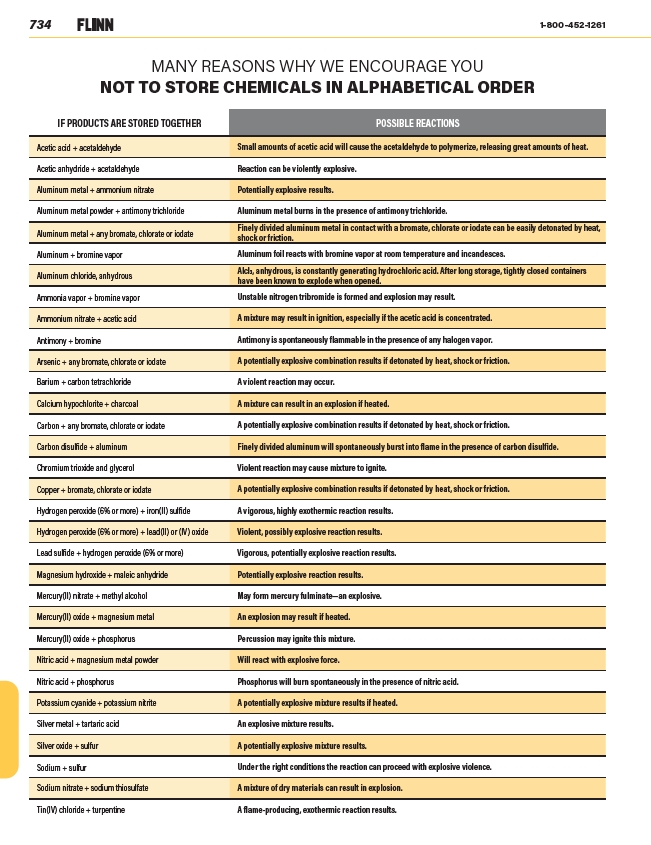
MANY REASONS WHY WE ENCOURAGE YOU
NOT TO STORE CHEMICALS IN ALPHABETICAL ORDER
IF PRODUCTS ARE STORED TOGETHER POSSIBLE REACTIONS
Acetic acid + acetaldehyde Small amounts of acetic acid will cause the acetaldehyde to polymerize, releasing great amounts of heat.
Acetic anhydride + acetaldehyde Reaction can be violently explosive.
Aluminum metal + ammonium nitrate Potentially explosive results.
Aluminum metal powder + antimony trichloride Aluminum metal burns in the presence of antimony trichloride.
Aluminum metal + any bromate, chlorate or iodate
Finely divided aluminum metal in contact with a bromate, chlorate or iodate can be easily detonated by heat,
shock or friction.
Aluminum + bromine vapor Aluminum foil reacts with bromine vapor at room temperature and incandesces.
Aluminum chloride, anhydrous
Alcl3, anhydrous, is constantly generating hydrochloric acid. After long storage, tightly closed containers
have been known to explode when opened.
Ammonia vapor + bromine vapor Unstable nitrogen tribromide is formed and explosion may result.
Ammonium nitrate + acetic acid A mixture may result in ignition, especially if the acetic acid is concentrated.
Antimony + bromine Antimony is spontaneously flammable in the presence of any halogen vapor.
Arsenic + any bromate, chlorate or iodate A potentially explosive combination results if detonated by heat, shock or friction.
Barium + carbon tetrachloride A violent reaction may occur.
Calcium hypochlorite + charcoal A mixture can result in an explosion if heated.
Carbon + any bromate, chlorate or iodate A potentially explosive combination results if detonated by heat, shock or friction.
Carbon disulfide + aluminum Finely divided aluminum will spontaneously burst into flame in the presence of carbon disulfide.
Chromium trioxide and glycerol Violent reaction may cause mixture to ignite.
Copper + bromate, chlorate or iodate A potentially explosive combination results if detonated by heat, shock or friction.
Hydrogen peroxide (6% or more) + iron(II) sulfide A vigorous, highly exothermic reaction results.
Hydrogen peroxide (6% or more) + lead(II) or (IV) oxide Violent, possibly explosive reaction results.
Lead sulfide + hydrogen peroxide (6% or more) Vigorous, potentially explosive reaction results.
Magnesium hydroxide + maleic anhydride Potentially explosive reaction results.
Mercury(II) nitrate + methyl alcohol May form mercury fulminate—an explosive.
Mercury(II) oxide + magnesium metal An explosion may result if heated.
Mercury(II) oxide + phosphorus Percussion may ignite this mixture.
Nitric acid + magnesium metal powder Will react with explosive force.
Nitric acid + phosphorus Phosphorus will burn spontaneously in the presence of nitric acid.
Potassium cyanide + potassium nitrite A potentially explosive mixture results if heated.
Silver metal + tartaric acid An explosive mixture results.
Silver oxide + sulfur A potentially explosive mixture results.
Sodium + sulfur Under the right conditions the reaction can proceed with explosive violence.
Sodium nitrate + sodium thiosulfate A mixture of dry materials can result in explosion.
Tin(IV) chloride + turpentine A flame-producing, exothermic reaction results.